[ad_1]
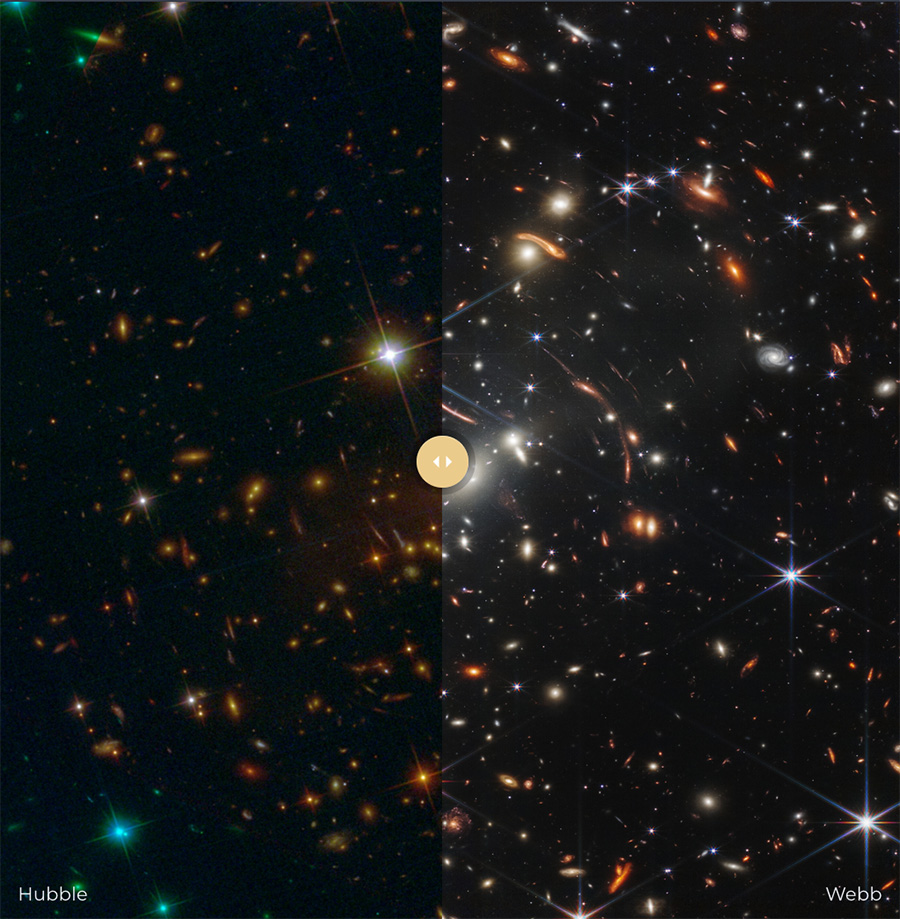
John Christensen / WebbCompare
Maybe you’ve heard: The James Webb Area Telescope (JWST) is the newest and best observatory in area, wowing the astronomical group with superb photographs launched final week.
However amid all the joy, the Hubble Area Telescope — NASA’s orbital transformational observatory now for greater than 32 years — continues its exploration and discovery.
“We consider that we are able to maintain Hubble doing the ground-breaking science it’s identified for by means of the latter a part of this decade and probably into the following,” says public affairs officer Claire Andreoli (NASA Goddard).
Hubble: From Hassle to Triumph
Deployed on April 25, 1990, from the cargo bay of the U.S. area shuttle Discovery, Hubble acquired off to a rocky begin: A faulty mirror wasn’t found till after deployment and calibration. Three years later, astronauts repaired the defect with “corrective lenses,” named the Corrective Optics Area Telescope Axial Substitute (COSTAR) bundle, which they positioned within the telescope throughout the STS-61/Servicing Mission One.
4 servicing missions adopted, every one deploying upgrades and new devices, however the Atlantis STS-125 mission in 2009 could be the final: Hubble is now by itself. Regardless of some scares, together with a short laptop glitch final 12 months, Hubble’s doing simply wonderful.
NASA
“Hubble remains to be going sturdy and continues to have an necessary and distinctive position to play in innovative astronomy analysis,” says Misty Bentz (Georgia State College) “It additionally stays common with astronomy researchers, as the newest name for proposals in March 2022 obtained 5 occasions the variety of proposal requests that may very well be accommodated!”
Hubble’s 2022 Highlights
Hubble’s observations over the 12 months have helped scientists decide the speed of the universe’s enlargement, establish moons of Pluto, and make clear unique worlds. (See “Celebrating 30 Years” for a few of Hubble’s most mesmerizing photographs.)
Even on this 12 months alone, Hubble has damaged information whereas capturing gorgeous imagery:
- Hubble not too long ago found essentially the most distant star identified, dubbed Earendel. The pictures present Earendel because it was 12.9 billion years in the past, solely 900 million years after the Huge Bang.
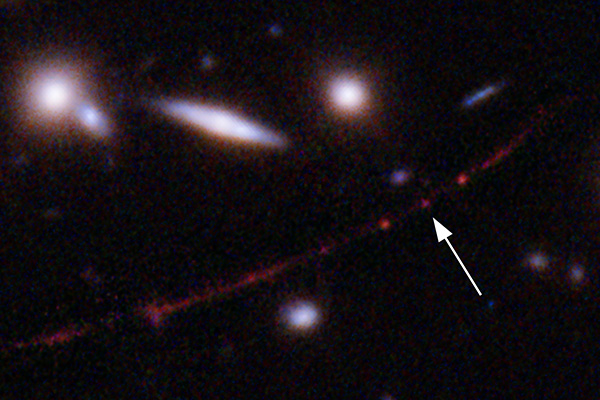

Science: NASA / ESA / Brian Welch (JHU) / Dan Coe (STScI)
- The telescope continues to seize gorgeous views, resembling this deep stare on the globular cluster Terzan 2 in Scorpius:
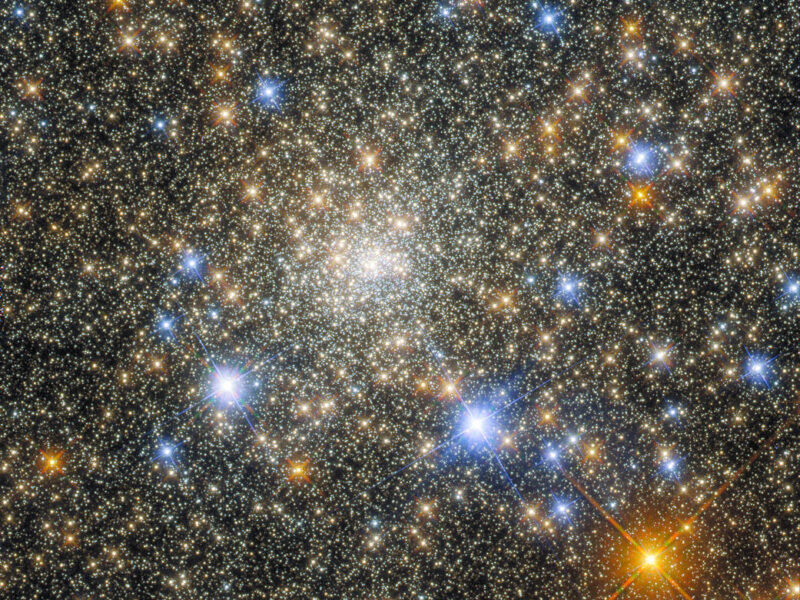

HST / NASA / GFSC / STScI
- The mission additionally not too long ago imaged Comet Bernardinelli-Bernstein (C/2014 UN271), confirming that it is the most large Oort Cloud comet identified. The brand new observations present that its nucleus is an estimated 137 kilometers (85 miles) throughout. Comet Bernardinelli-Bernstein will attain perihelion exterior the orbit of Saturn in 2031.

HST / NASA / GSFC / STScI
Webb’s Complement
Hubble has an necessary position play within the new JWST period, as a result of regardless that Webb was typically billed as Hubble’s successor, the 2 telescopes are literally fairly totally different.

NASA
“Hubble supplies high-resolution ultraviolet and visual imaging and spectroscopy, whereas JWST is optimized for the infrared,” Bentz says. “Hubble continues to dominate in research of close by stars and galaxies, in addition to accreting supermassive black holes.”
In reality, Bentz is main a brand new program that makes use of Hubble to detect Cepheid variables in three galaxies, as a way to decide their distances. “Cepheids are most variable at blue wavelengths, the place JWST can’t observe,” Bentz explains. “Moreover, JWST could be very gradual to maneuver from one goal to a different, so it’s not optimized for returning to the identical goal repeatedly, as is required in research of variable objects like Cepheids.”
There are additionally plans afoot to make the most of Hubble for complementary, simultaneous observations with different observatories, together with JWST. Such multiwavelength observations might help acquire an understanding that research in ultraviolet, seen, or infrared alone can’t.
For instance, Bentz factors to the neutron star merger that the LIGO and Virgo Collaborations detected in 2017. “Astronomers all over the world collected observations at each wavelength doable to study as a lot as we may concerning the bodily processes occurring throughout the collision and its messy aftermath,” Bentz says.
Hubble’s Destiny
In its most up-to-date overview of Hubble operations, NASA introduced that it will help the observatory by means of June 2026. In reality, present estimates recommend the observatory can keep in a high-enough orbit for operations to proceed till the mid-2030s and past; its photo voltaic arrays and batteries are additionally in nice form.
The limiting issue comes all the way down to the gyros that the area telescope makes use of to show and lock onto targets. Whereas nearly all of the observatory’s programs are redundant, which means there’s nonetheless a back-up accessible if one piece fails, the gyros are one of many few exceptions. Hubble launched with six, however three have failed.
“The telescope is presently working with three gyros and no spares,” Andreoli says. Nevertheless, whereas it takes three gyros to allow environment friendly operations, observations are nonetheless doable, albeit much less environment friendly, with just one gyro.
Engineers have discovered intelligent methods to maintain missions going effectively previous their guarantee: Witness the “heat” mission on Spitzer when its coolant ran out, or Kepler’s prolonged K2 mission after the second of its 4 response wheels failed. Likewise, after the payload laptop gave Hubble issues final summer season, crew engineers acquired issues again up and working, and so they’re nonetheless working to enhance operational processes.
As soon as the Hubble mission ends, hopefully a very long time from now, NASA plans to convey it down in a managed method. On the final servicing mission, astronauts put in a Gentle Seize Mechanism on the bottom of Hubble. It may very well be utilized by a robotic mission to spice up the telescope’s orbit, however extra doubtless it’ll put together it for a managed reentry when the time comes.

NASA / GSFC
Whereas it is nonetheless up there, you may be capable to see Hubble in orbit: The telescope is in a 28.5°-inclination orbit, which means it’s a frequent naked-eye sight for observers at latitudes between 35 °S and 35°N, which incorporates the southern a part of the US.
A complete technology of astronomers have come of age with Hubble in area, and it stays a significant part within the toolbox of contemporary astronomers. Count on extra nice science to return from this venerable area telescope.

Commercial
[ad_2]



