[ad_1]
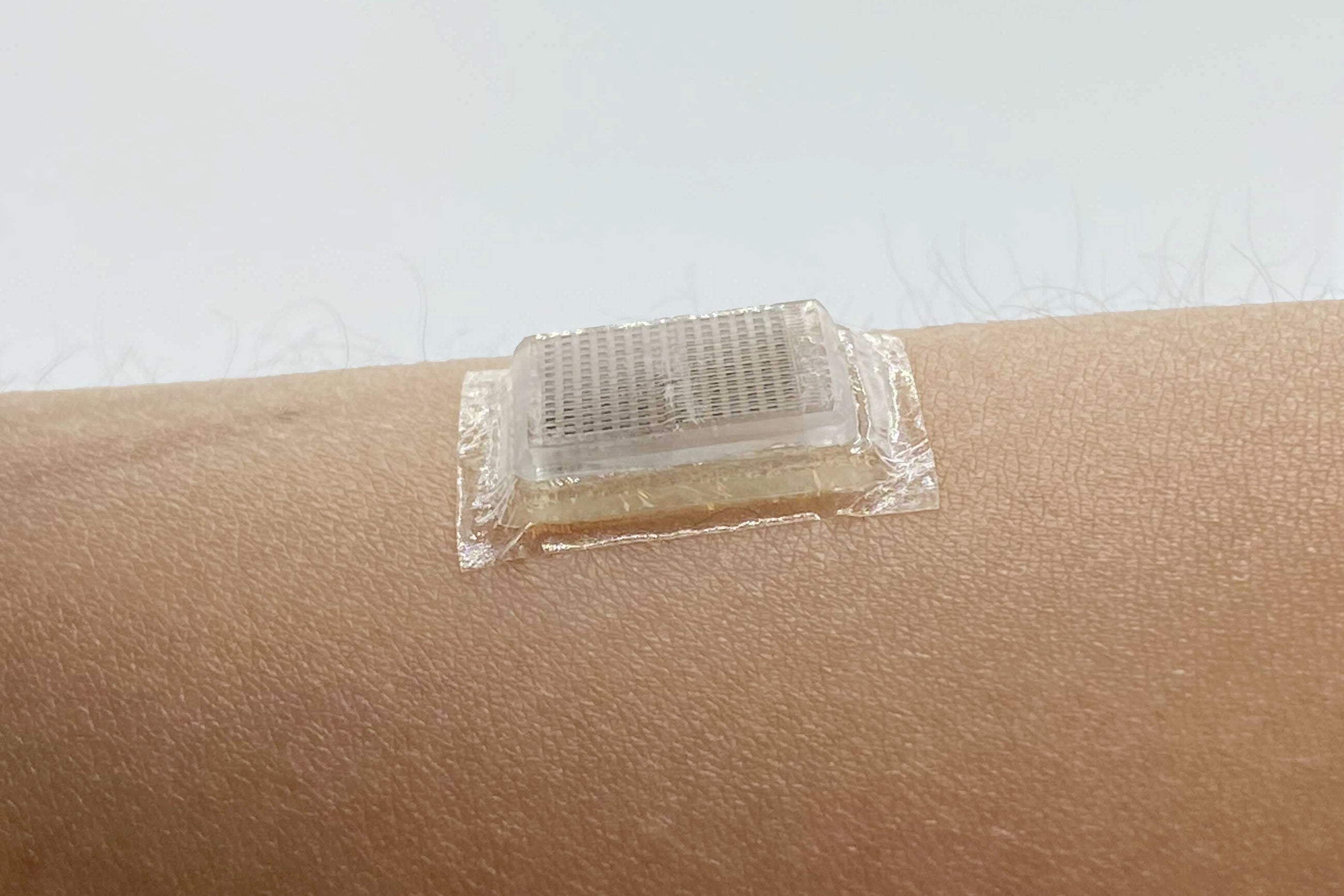
Ultrasound scanners, which picture the within of the human physique, are a life-saving medical device. Now researchers have shrunk the hand-held ultrasound probe—which generally requires a extremely skilled technician to maneuver over the pores and skin—all the way down to a flat chip that’s the dimension of a postage stamp and sticks to the pores and skin with a particular bioadhesive. The new machine can file high-resolution movies for 2 days at a stretch, capturing blood vessels and hearts laboring throughout train or stomachs increasing and shrinking as check topics gulp juice after which digest it.
“The fantastic thing about that is, immediately, you may adhere this ultrasound probe, this skinny ultrasound speaker, to the physique over 48 hours,” says Xuanhe Zhao, a mechanical engineer on the Massachusetts Institute of Expertise and co-author of a paper describing the brand new machine, which was printed in Science on Thursday. By recording nonetheless photos and movies of inside organs throughout this time, a wearable imaging machine could possibly be used to diagnose coronary heart assaults and malignant tumors, check the effectiveness of medicines and assess common coronary heart, lung or muscle well being. “This may probably change the paradigm of medical imaging by empowering long-term steady imaging,” Zhao provides, “and it may possibly change the paradigm of the sphere of wearable gadgets.”
Conventional ultrasounds are nice at peering beneath the pores and skin with out inflicting harm to the physique, however entry to such scans is proscribed. “The traditional handheld ultrasound requires well-trained technicians to place the probe correctly on the pores and skin and apply some liquid gel between the probe and pores and skin,” says Nanshu Lu, a mechanical engineer on the College of Texas at Austin, who was not concerned within the new analysis however co-wrote an accompanying evaluation in Science. “And as you may think about, it’s fairly tedious and really short-term, very constrained.” As a result of they require an skilled human operator, Lu explains, these scans are costly, they usually can’t be utilized in checks the place the topic is exercising or placing their physique underneath stress from warmth or excessive environments. “Standard ultrasounds have lots of limitations,” she says. “If we are able to make ultrasound sensors wearable and cell and accessible, it would open lots of new potentialities.”
Due to their potential versatility, different researchers have tried to make stick-on ultrasound patches. However with the intention to adhere to smooth, stretchy pores and skin, earlier gadgets have been designed to be stretchable themselves. This manner issue weakened picture high quality as a result of it couldn’t accommodate as many transducers—items that, on this case, remodel electrical energy into sound waves with frequencies too excessive for human ears to detect. An ultrasound probe sends these waves by means of a layer of gooey gel into the human physique, the place they bounce off organs and different inside buildings after which return to the transducer array. This converts the mechanical waves again to electrical indicators and sends them to a pc for translation into pictures.
The extra transducers, the higher the picture high quality. “It’s similar to a digital camera,” explains Philip Tan, {an electrical} engineer and a graduate pupil at Lu’s lab at U.T. Austin, who was additionally not concerned with the brand new examine however co-wrote the evaluation piece. A stretchy stick-on ultrasound probe, which should be capable of flex each time the pores and skin strikes, can not pack as many transducers into the array—and when the wearer strikes, the configuration of transducers shifts and makes it troublesome to seize steady pictures.
As a substitute of creating the machine itself stretchy, Zhao and his crew hooked up a inflexible probe, simply three millimeters thick, to a versatile layer of adhesive. This adhesive replaces the gooey liquid positioned between a conventional ultrasound wand and the pores and skin, and it’s a hybrid of a water-rich polymer referred to as a hydrogel and a rubberlike materials referred to as an elastomer. “It’s a piece of strong hydrogel containing over 90 % water, however it’s in a strong state like Jell-O,” Zhao says. “We cowl the floor of this Jell-O with this very skinny membrane of elastomer in order that the water contained in the Jell-O won’t evaporate out.” This bioadhesive not solely caught the probe firmly to the pores and skin for 48 hours, but it surely additionally supplied a cushioning layer that protected the inflexible electronics from the flexing of pores and skin and muscle mass.
To picture totally different physique techniques, Zhao’s crew examined variations of the probe that produce waves at totally different frequencies and thus penetrate the physique to totally different depths. As an example, a excessive frequency comparable to 10 megahertz may make it to a few centimeters beneath the pores and skin. The researchers used this frequency to seize the motion of blood vessels and muscle mass as check topics shifted from sitting to standing or exercised vigorously. A decrease frequency of three megahertz goes deeper, extra like six centimeters, to seize inside organs. Utilizing this frequency, the researchers imaged the 4 chambers of a topic’s coronary heart, and recorded the abdomen of one other emptying out as their system processed a few cups of juice. The researchers additionally in contrast the photographs gathered with their inflexible ultrasound probe with these captured by a stretchable ultrasound machine, Zhao says. “You’ll be able to see the decision of ours is nearly one order of magnitude [10 times] larger than the stretchable ultrasound,” he provides.
An imaging machine that maintains a steady watch over particular elements of the physique could possibly be used to watch and diagnose a wide range of illnesses. Medical doctors may preserve an in depth eye on the progress of a tumor over time. Somebody at excessive threat of hypertension may put on an ultrasound patch to measure their hypertension, alerting them when the strain spikes or monitoring whether or not a drugs helps. A COVID affected person may keep dwelling, understanding that an imaging machine would alert them if their sickness induced a lung an infection extreme sufficient to require hospitalization. Maybe an important utility could possibly be within the detection and analysis of coronary heart assaults. “Heart problems is … the main explanation for loss of life in the entire world, additionally within the U.S.,” Zhao says. Coronary heart well being is on the radar of different wearable machine builders. As an example, good watches such because the Apple Watch are able to monitoring {the electrical} indicators that point out coronary heart exercise with a so-called electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This can be utilized to diagnose coronary heart assaults—at the very least in some circumstances. “There are already research exhibiting that EKG can solely diagnose round 20 % of coronary heart assaults. The vast majority of coronary heart assaults truly require imaging modalities, comparable to ultrasound imaging, to diagnose,” Zhao says. Steady imaging of a affected person’s coronary heart may seize their signs and supply an early analysis.
“The large promoting level of this new machine is that it opens new varieties of medical analysis that may’t be performed in a static setting,” Tan says. To evaluate coronary heart well being, as an illustration, it’s useful to measure the organ’s exercise whereas exercising—but it surely’s onerous to carry an ultrasound wand in opposition to a operating topic’s goo-covered chest. “With a wearable ultrasound patch, the place you wouldn’t have to carry the transducer on the individual, they have been truly in a position to present that you simply’re in a position to get very high-quality pictures of the guts even throughout movement,” Tan provides.
The bioadhesive machine will not be prepared for motion but, nonetheless. For one factor, it nonetheless needs to be bodily plugged into a pc that may accumulate and analyze the information the probe produces. “We join this probe by means of a wire to an information acquisition system,” Zhao says. “However my group is working very onerous to miniaturize and combine every little thing into our wi-fi machine.” He in the end plans to improve the patch with a miniaturized energy supply and a wi-fi data-transmission system. This can be a possible purpose, Lu and Tan agree, because of shrinking digital parts and fabrication strategies that enable these options to be mixed into an “ultrasound on a chip.” Lu means that if the sphere can appeal to federal and personal investments, such a tool could possibly be possible inside 5 years, though it could nonetheless should earn approval from federal regulators.
In the end, ultrasound stickers may be part of the ranks of wearables that monitor human well being, together with current gadgets that collect details about coronary heart fee, sleep high quality and even stress. “Our human physique is radiating lots of a extremely private, extremely steady, distributed and multimodal information about our well being, our emotion, our consideration, our readiness, and so forth. So we’re full of information,” Lu says. “The query is methods to get them reliably and repeatedly.”
[ad_2]



